# Observer 观察者模式
一个对象(称为 subject)维持一系列依赖于它(观察者)的对象,将有关状态的任何变更自动通知给它们
- Subject: 目标,维护一系列的观察者,方便添加或删除观察者
- Observer: 观察者,为那些在目标状态发生改变时或得通知的对象提供一个更新接口
- ConcreteSubject: 具体目标,状态发生改变时,向 Observer 发出通知,储存 ConcreteObserver 的状态
- ConcreteObserver: 具体观察者,存储一个指向 ConcreteSubject 的引用,实现 Observer 的更新接口,以实现自身状态与目标的状态保持一致
# Observer 观察者模式实现
// 观察者列表
function ObserverList () {
this.observerList = []
}
ObserverList.prototype.Add = function (obj) {
this.observerList.push(obj)
}
ObserverList.prototype.Empty = function () {
this.observerList = []
}
ObserverList.prototype.Count = function () {
return this.observerList.length
}
ObserverList.prototype.Get = function (index) {
if (index > -1 && index < this.observerList.length) {
return this.observerList[index]
}
return null
}
ObserverList.prototype.Insert = function (obj, index) {
let pointer = -1
pointer = Max.max(index, 0)
pointer = Math.min(index, this.observerList.length)
this.observerList = [...this.observerList.slice(0, index), obj, ...this.observerList.slice(index)]
return pointer
}
ObserverList.prototype.IndexOf = function (obj, startIndex) {
var i = startIndex
var pointer = -1
while (i < this.observerList.length) {
if (this.observerList[i] === obj) {
pointer = i
break
}
i++
}
return pointer
}
ObserverList.prototype.RemoveIndexAt = function (index) {
let pointer = -1
pointer = Max.max(index, 0)
pointer = Math.min(index, this.observerList.length)
this.observerList.splice(pointer, 1)
}
function extend (obj, extension) {
for (var key in obj) {
extension[key] = obj[key]
}
}
// Subject 维护一系列的观察者
function Subject () {
this.observers = new ObserverList()
}
Subject.prototype.AddObserver = function (observer) {
this.observers.Add(observer)
}
Subject.prototype.RemoveObserve = function (observer) {
this.observers.RemoveIndexAt(this.observers.IndexOf(observer, 0))
}
Subject.prototype.Notify = function (context) {
var observerCount = this.observers.Count()
for (let i = 0; i < observerCount; i++) {
this.observers.Get(i).Update(context)
}
}
// Observer
function Observer () {
this.update = function () {
console.log('get notify')
throw new Error('the update method thould be defined by the observer')
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
使用上述功能:
<button id="addNewObserver">Add new Observer checkbox</button>
<input type="checkbox" id="mainCheckbox">
<div id="observersContainer"></div>
1
2
3
2
3
var controlCheckbox = document.getElementById('mainCheckbox')
var addBtn = document.getElementById('addNewObserver')
var container = document.getElementById('observersContainer')
// 具体目标 Concrete Subject
// 利用 Subject 拓展 controlCheckbox
extend(new Subject(), controlCheckbox)
// 点击 checkbox 会触发通知到观察者上
controlCheckbox['onclick'] = function () {
controlCheckbox.Notify(controlCheckbox.checked)
}
addBtn['onclick'] = AddNewObserver
function AddNewObserver() {
// 创建需要添加的新 checkbox
var check = document.createElement('input')
check.type = 'checkbox'
extend(new Observer(), check)
// 重写更新行为
check.Update = function (value) {
this.checked = value
}
controlCheckbox.AddObserver(check)
container.appendChild(check)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# Observer 观察者模式和 Publish/Subscribe 发布/订阅 模式的区别
Observer 模式要求希望接收到主题通知的观察者(或者对象)必须订阅内容改变的事件
Publish/Subscribe 模式使用了一个 主题/事件 通道,这个通道介于希望接收到通知(订阅者)的对象和激活事件的对象(发布者)之间。该事件系统允许代码定义应用程序的特定事件,这些事件可以传递自定义参数,自定义参数包含订阅者所需要的值。其目的在于避免订阅者与发布者之间产生依赖关系。
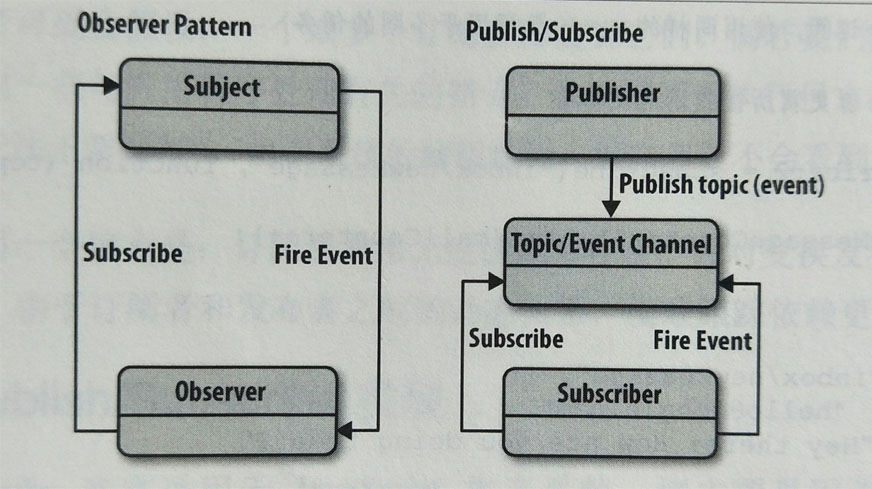
优点:Observer 模式和 Publish/Subscribe 模式鼓励我们努力思考应用程序不同部分之间的关系。无需使类紧密耦合
缺点:如果订阅者执行日志奔溃了,发布者无法看到。订阅者非常无视彼此的存在,并对变换发布者产生的成本视而不见。由于订阅者和发布者之间的动态关系,很难跟踪依赖更新。
# Publish/Subscribe 实现